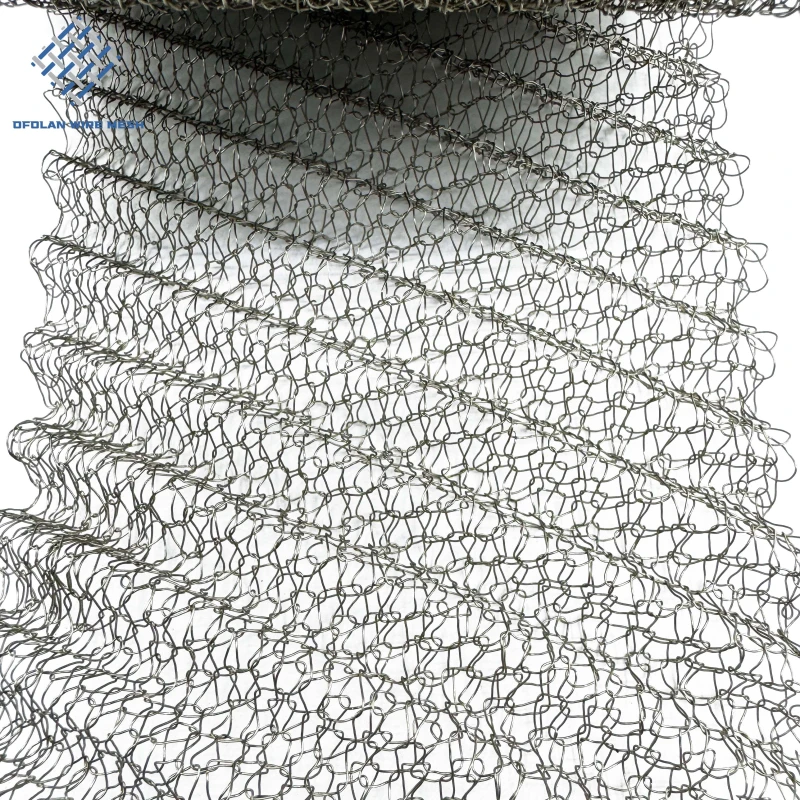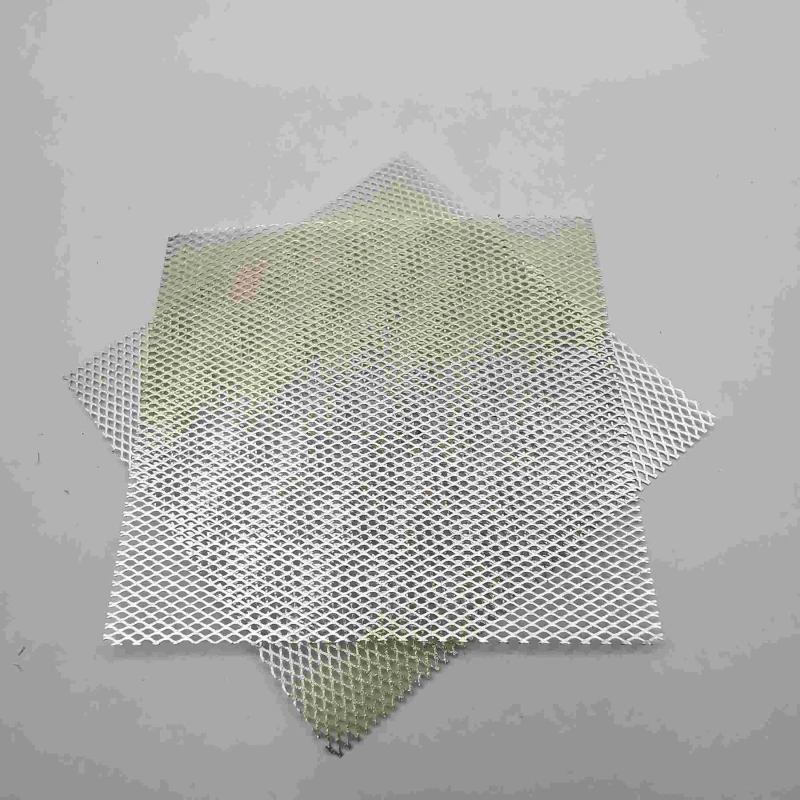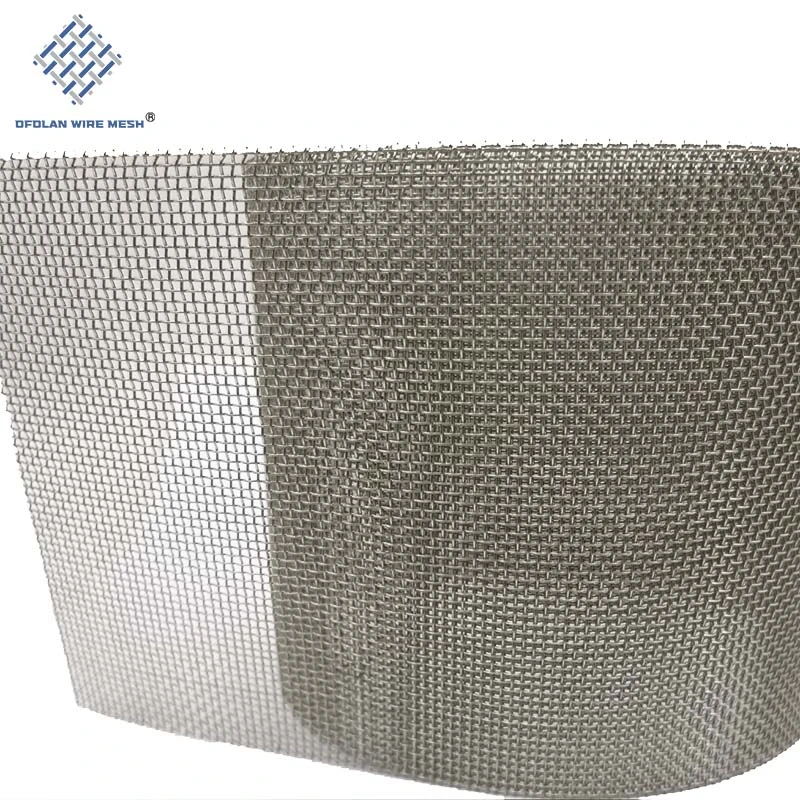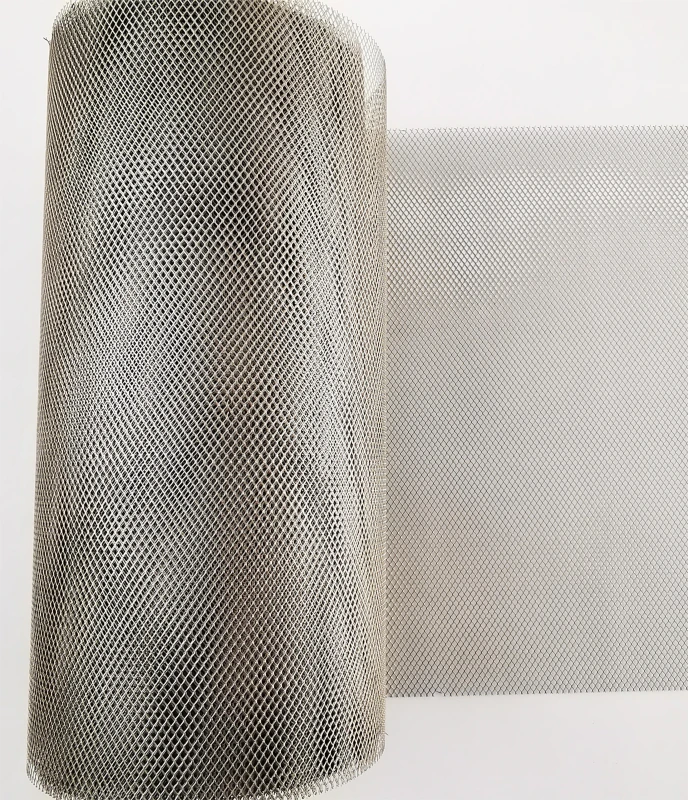















Low-Volatility Molybdenum Mesh for Vacuum Coating & Deposition Systems

Reviews & Ratings
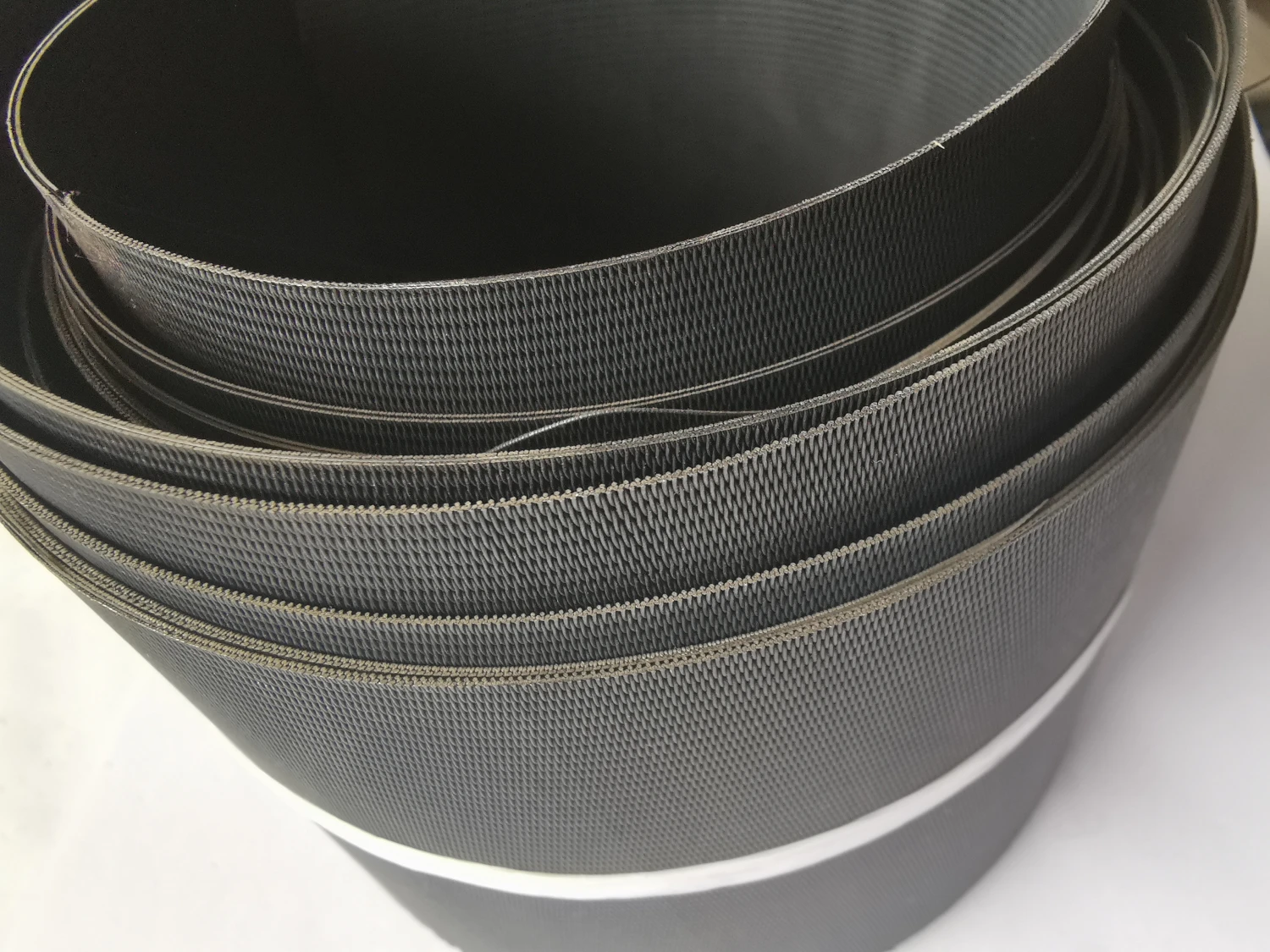
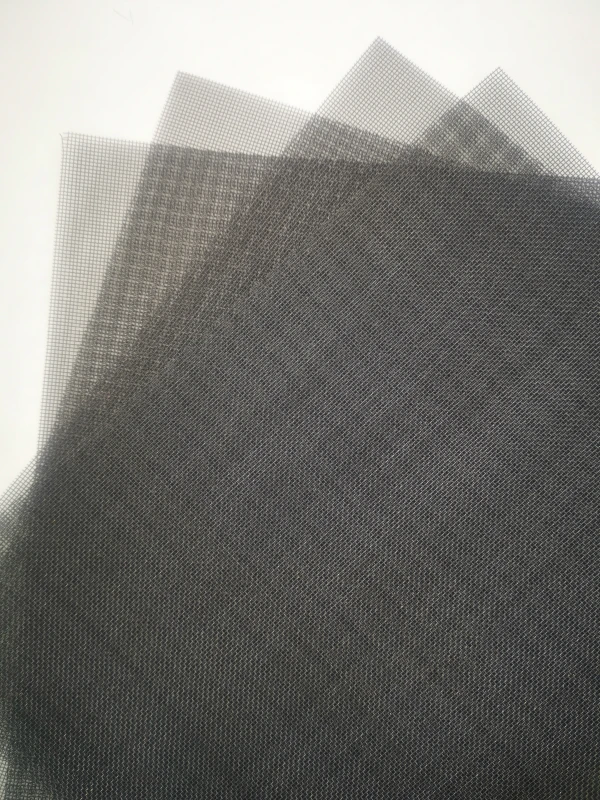
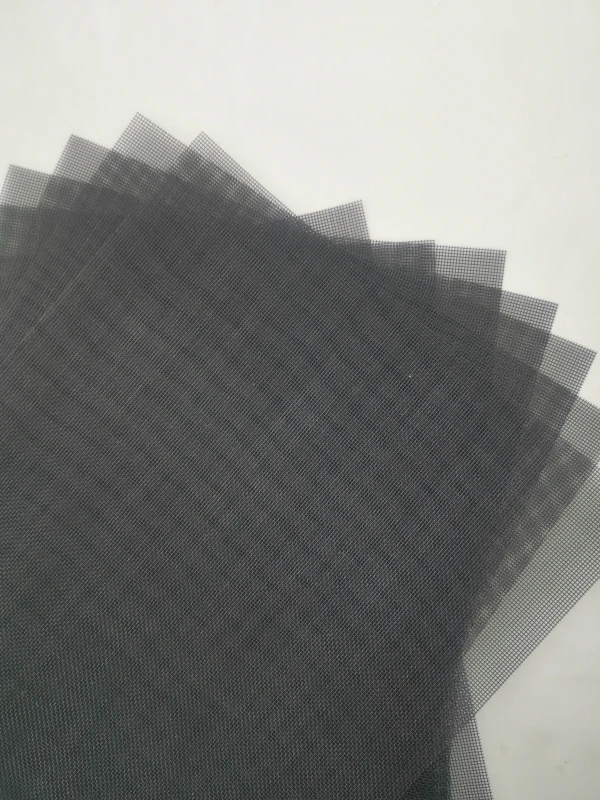
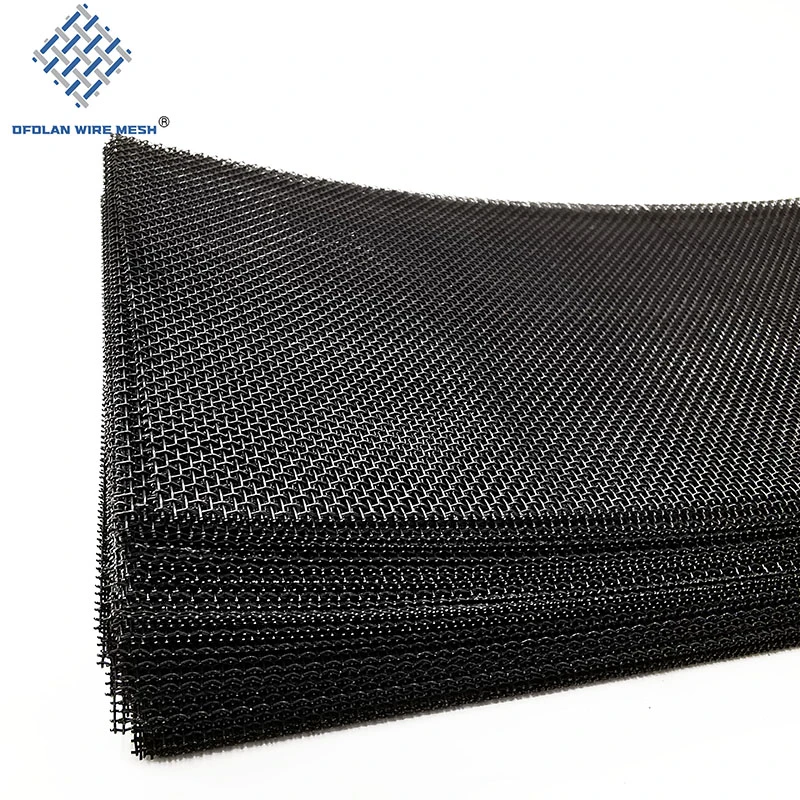
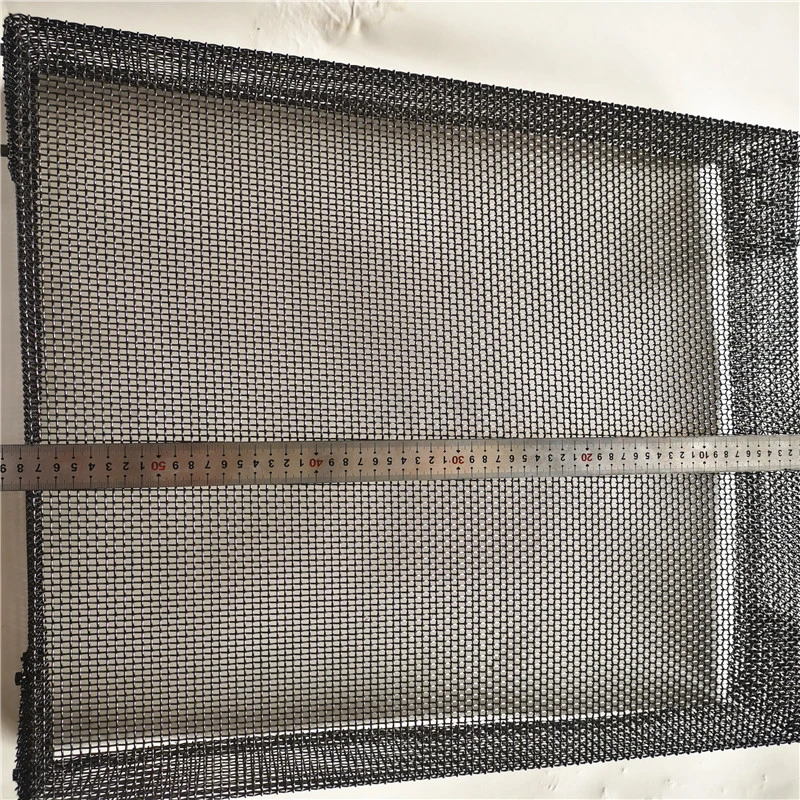
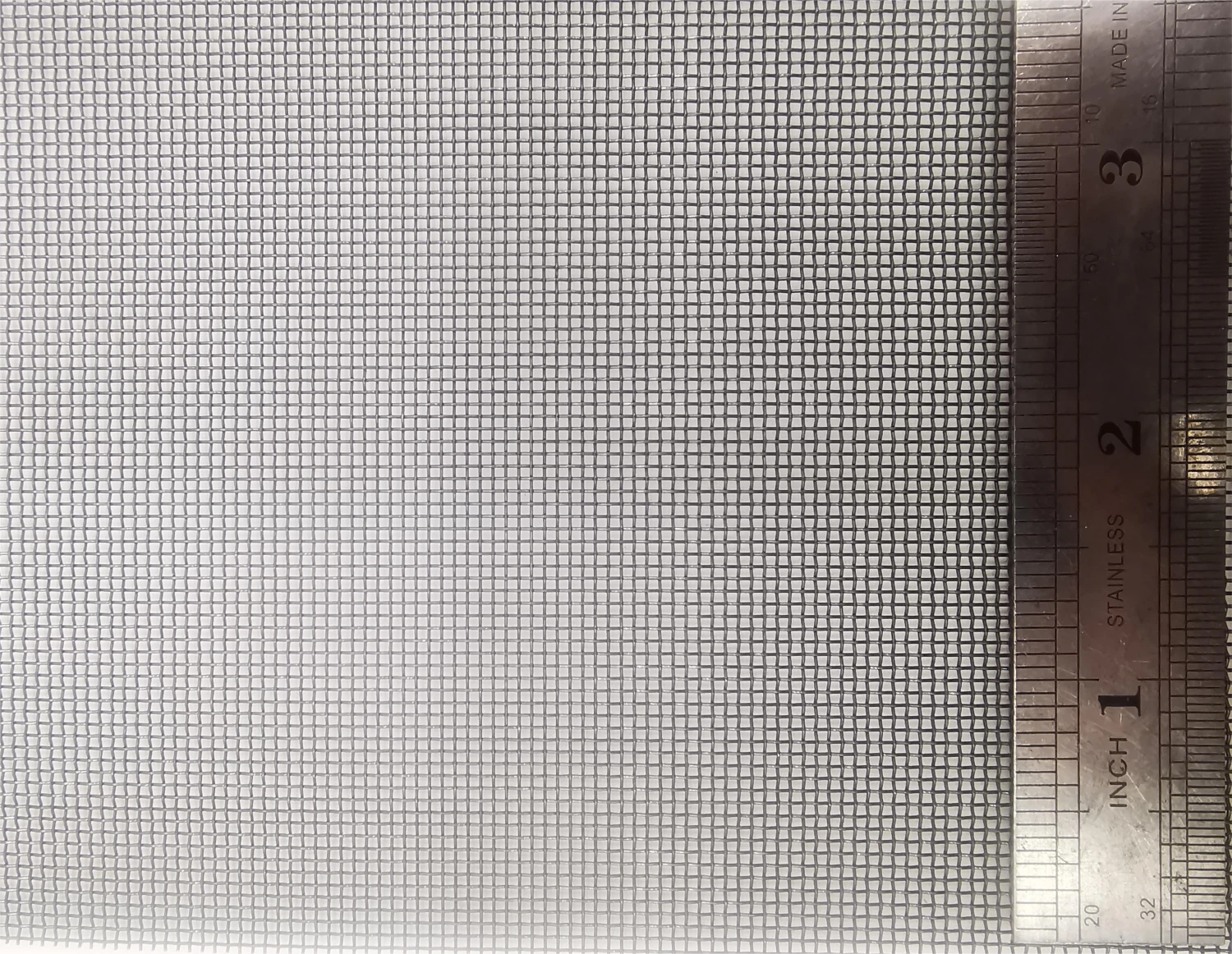
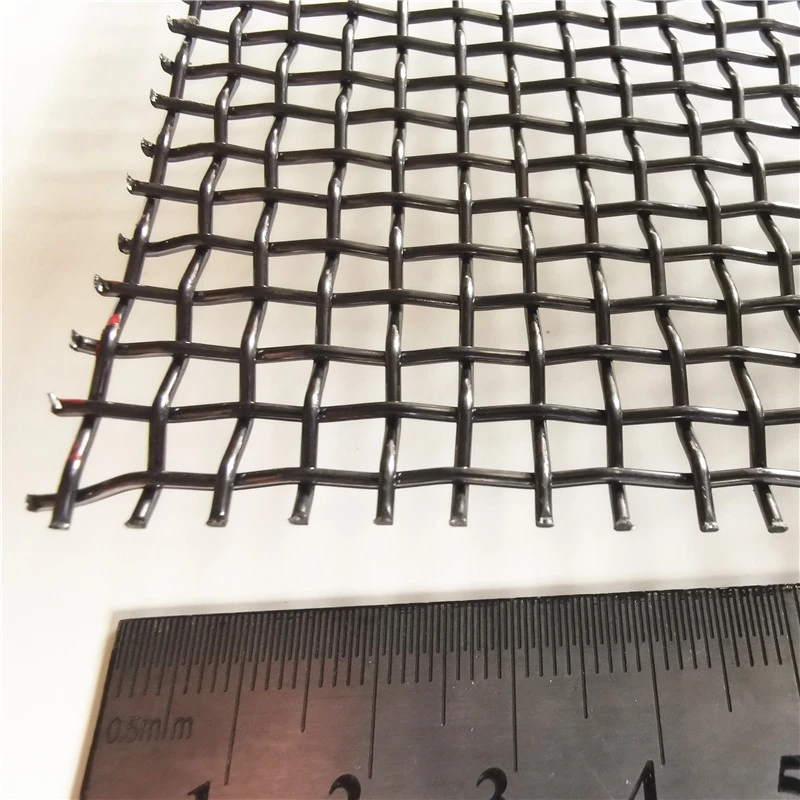
Product Name |
|
Model | MO1>99.95% Molybdenum Rhenium Alloy |
Density | 10.22 g/cm3 |
Melting Point | 2610 ℃ |
Characteristic | At room temperature, molybdenum mesh is stable in both air and water, and does not work on hydrochloric acid, hydrofluoric acid, dilute nitric acid, and alkaline solutions. 2. When used in a vacuum environment, uncoated molybdenum has a very long service life. Molybdenum is completely stable in pure hydrogen, argon, and helium. Molybdenum does not undergo a chemical reaction with hydrogen until its melting temperature. But when molybdenum is heated in hydrogen gas, it can absorb a portion of the hydrogen gas to form a solid solution. For example, at 1000 ℃, 100 grams of molybdenum metal can dissolve 0.5 cubic centimeters of hydrogen. The application of molybdenum mesh in many electric furnaces fully demonstrates this characteristic. Above 1500 ℃, molybdenum mesh reacts chemically with nitrogen to form nitrides. If the pressure of nitrogen is very low (about 0.01 mmHg), it cannot be seen even at 2400 ℃. Molybdenum mesh still exhibits considerable properties in carbon dioxide, ammonia, and nitrogen up to approximately 1100 ℃. At higher temperatures, nitride films may form on the surface of molybdenum mesh in ammonia and nitrogen gas. At temperatures above 1100 ℃, it can be carbonized by carbon containing gases such as hydrocarbons and carbon monoxide. |
Application | Molybdenum mesh is widely used in vacuum high-temperature furnace sintering of neodymium iron boron support mesh, as a connecting component in corrosion-resistant production, structural components working in high-temperature environments, heating elements, integrated circuits, gas filtration, aerospace, military and other fields. |
Contact Information | M. P:+86-13315865785 Email:estrellayue@ofolan.com WhatsApp:+86-13315865785 |
Frequently Bought Products
Product Queries (0)
Login Or Registerto submit your questions to seller
Other Questions
No none asked to seller yet